Menu
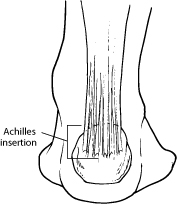
The Achilles tendon – where Achilles tendon disorders occur – is the band of tissue that runs down the back of the lower leg, connecting the calf muscle to the heel bone. Also called the heel cord, the Achilles tendon facilitates walking by helping to raise the heel off the ground.
Two common disorders that occur in the heel cord are Achilles tendonitis and Achilles tendonosis.
Achilles tendonitis is an inflammation of the Achilles tendon. This inflammation is typically short-lived. Over time, if not resolved, the condition may progress to a degeneration of the tendon (Achilles tendonosis), in which the tendon loses its organized structure and is likely to develop microscopic tears. Sometimes the degeneration involves the site where the Achilles tendon attaches to the heel bone. In rare cases, chronic degeneration with or without pain may result in rupture of the tendon.
As “overuse” disorders, Achilles tendonitis and tendonosis are usually caused by a sudden increase of a repetitive activity involving the Achilles tendon. Such activity puts too much stress on the tendon too quickly, leading to micro-injury of the tendon fibers. Due to this ongoing stress on the tendon, the body is unable to repair the injured tissue. The structure of the tendon is then altered, resulting in continued pain.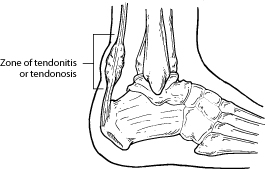
Athletes are at high risk for developing disorders of the Achilles tendon. Achilles tendonitis and tendonosis are also common in individuals whose work puts stress on their ankles and feet, such as laborers, as well as in “weekend warriors”—those who are less conditioned and participate in athletics only on weekends or infrequently.
In addition, people with excessive pronation (flattening of the arch) have a tendency to develop Achilles tendonitis and tendonosis due to the greater demands placed on the tendon when walking. If these individuals wear shoes without adequate stability, their overpronation could further aggravate the Achilles tendon.
The symptoms associated with Achilles tendonitis and tendonosis include:
In diagnosing Achilles tendonitis or tendonosis, the surgeon will examine the patient’s foot and ankle and evaluate the range of motion and condition of the tendon. The extent of the condition can be further assessed with x-rays or other imaging modalities.
Treatment approaches for Achilles tendonitis or tendonosis are selected on the basis of how long the injury has been present and the degree of damage to the tendon. In the early stage, when there is sudden (acute) inflammation, one or more of the following options may be recommended:
If nonsurgical approaches fail to restore the tendon to its normal condition, surgery may be necessary. The foot and ankle surgeon will select the best procedure to repair the tendon, based on the extent of the injury, the patient’s age and activity level, and other factors.
To prevent Achilles tendonitis or tendonosis from recurring after surgical or nonsurgical treatment, the foot and ankle surgeon may recommend strengthening and stretching of the calf muscles through daily exercises. Wearing proper shoes for the foot type and activity is also important in preventing recurrence of the condition.
Foot and ankle surgeons are the leading experts in foot and ankle care today. As doctors of podiatric medicine – also known as podiatrists, DPMs or occasionally “foot and ankle doctors” – they are the board-certified surgical specialists of the podiatric profession. Foot and ankle surgeons have more education and training specific to the foot and ankle than any other healthcare provider.
Foot and ankle surgeons treat all conditions affecting the foot and ankle, from the simple to the complex, in patients of all ages including Achilles tendon disorders. Their intensive education and training qualify foot and ankle surgeons to perform a wide range of surgeries, including any surgery that may be indicated for Achilles tendon disorders.